Application#
See also
For more detailed information about Gtk.Application checkout the
Using GtkApplication tutorial.
Gtk.Application is the foundation for creating GTK apps. It encompasses
many repetitive tasks that a modern application needs such as handling multiple
instances, D-Bus activation, opening files, command line parsing,
startup/shutdown, menu management, window management, and more.
In this example we will be also using Gtk.ApplicationWindow, it
provides some extra features over regular Gtk.Window for main
application windows.
Actions#
Gio.Action is a way to expose any single task your application or widget
does by a name. These actions can be disabled/enabled at runtime and they can
either be activated or have a state changed (if they contain state).
The reason to use actions is to separate out the logic from the UI. For example
this allows using a menubar on OSX and a gear menu on GNOME both simply
referencing the name of an action. On the main implementation of this, what you will
be using is Gio.SimpleAction, which will be demonstrated later.
Many classes such as Gio.MenuItem and Gtk.Actionable interface
implementations like Gtk.Button support properties to set an action
name.
These actions can be grouped together into a Gio.ActionGroup and
when these groups are added to a widget with Gtk.Widget.insert_action_group()
they will gain a prefix. Such as “win” when added to a Gtk.ApplicationWindow.
You will use the full action name when referencing it such as “app.about” but when
you create the action it will just be “about” until added to the application.
You can also very easily make keybindings for actions by setting the accel
property in the Gio.Menu file or by using Gtk.Application.set_accels_for_action().
Command Line#
When creating your application it takes a flag property of Gio.ApplicationFlags.
Using this you can let it handle everything itself or have more custom behavior.
You can use HANDLES_COMMAND_LINE to allow custom behavior in Gio.Application.do_command_line().
In combination with Gio.Application.add_main_option() to add custom options.
Using HANDLES_OPEN will do the work of simply taking file arguments for you and
let you handle it in Gio.Application.do_open().
If your application is already open these will all be sent to the existing instance
unless you use NON_UNIQUE to allow multiple instances.
Example#
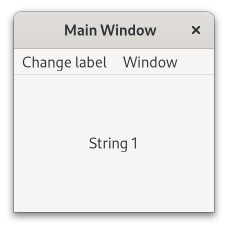
1import sys
2import gi
3
4gi.require_version("Gtk", "4.0")
5from gi.repository import GLib, Gio, Gtk
6
7# This would typically be its own file
8MENU_XML = """
9<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
10<interface>
11<menu id="menubar">
12 <submenu>
13 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">Change label</attribute>
14 <section>
15 <item>
16 <attribute name="action">win.change_label</attribute>
17 <attribute name="target">String 1</attribute>
18 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">String 1</attribute>
19 </item>
20 <item>
21 <attribute name="action">win.change_label</attribute>
22 <attribute name="target">String 2</attribute>
23 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">String 2</attribute>
24 </item>
25 <item>
26 <attribute name="action">win.change_label</attribute>
27 <attribute name="target">String 3</attribute>
28 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">String 3</attribute>
29 </item>
30 </section>
31 </submenu>
32 <submenu>
33 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">Window</attribute>
34 <section>
35 <item>
36 <attribute name="action">win.maximize</attribute>
37 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">Maximize</attribute>
38 </item>
39 </section>
40 <section>
41 <item>
42 <attribute name="action">app.about</attribute>
43 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">_About</attribute>
44 </item>
45 <item>
46 <attribute name="action">app.quit</attribute>
47 <attribute name="label" translatable="yes">_Quit</attribute>
48 <attribute name="accel"><Primary>q</attribute>
49 </item>
50 </section>
51 </submenu>
52</menu>
53</interface>
54"""
55
56
57class AppWindow(Gtk.ApplicationWindow):
58 def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
59 super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
60
61 self.set_default_size(200, 200)
62
63 # By default the title bar will be hide, let's show it
64 self.props.show_menubar = True
65
66 # This will be in the windows group and have the 'win' prefix
67 max_action = Gio.SimpleAction.new_stateful(
68 "maximize", None, GLib.Variant.new_boolean(False)
69 )
70 max_action.connect("change-state", self.on_maximize_toggle)
71 self.add_action(max_action)
72
73 # Keep it in sync with the actual state
74 self.connect(
75 "notify::maximized",
76 lambda obj, _pspec: max_action.set_state(
77 GLib.Variant.new_boolean(obj.props.maximized)
78 ),
79 )
80
81 lbl_variant = GLib.Variant.new_string("String 1")
82 lbl_action = Gio.SimpleAction.new_stateful(
83 "change_label", lbl_variant.get_type(), lbl_variant
84 )
85 lbl_action.connect("change-state", self.on_change_label_state)
86 self.add_action(lbl_action)
87
88 self.label = Gtk.Label(label=lbl_variant.get_string())
89 self.set_child(self.label)
90
91 def on_change_label_state(self, action, value):
92 action.set_state(value)
93 self.label.set_text(value.get_string())
94
95 def on_maximize_toggle(self, action, value):
96 action.set_state(value)
97 if value.get_boolean():
98 self.maximize()
99 else:
100 self.unmaximize()
101
102
103class Application(Gtk.Application):
104 def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
105 super().__init__(
106 *args,
107 application_id="org.example.App",
108 flags=Gio.ApplicationFlags.HANDLES_COMMAND_LINE,
109 **kwargs,
110 )
111 self.window = None
112
113 self.add_main_option(
114 "test",
115 ord("t"),
116 GLib.OptionFlags.NONE,
117 GLib.OptionArg.NONE,
118 "Command line test",
119 None,
120 )
121
122 def do_startup(self):
123 Gtk.Application.do_startup(self)
124
125 action = Gio.SimpleAction.new("about", None)
126 action.connect("activate", self.on_about)
127 self.add_action(action)
128
129 action = Gio.SimpleAction.new("quit", None)
130 action.connect("activate", self.on_quit)
131 self.add_action(action)
132
133 builder = Gtk.Builder.new_from_string(MENU_XML, -1)
134 self.set_menubar(builder.get_object("menubar"))
135
136 def do_activate(self):
137 # We only allow a single window and raise any existing ones
138 if not self.window:
139 # Windows are associated with the application
140 # when the last one is closed the application shuts down
141 self.window = AppWindow(application=self, title="Main Window")
142
143 self.window.present()
144
145 def do_command_line(self, command_line):
146 options = command_line.get_options_dict()
147 # convert GVariantDict -> GVariant -> dict
148 options = options.end().unpack()
149
150 if "test" in options:
151 # This is printed on the main instance
152 pass
153
154 self.activate()
155 return 0
156
157 def on_about(self, _action, _param):
158 about_dialog = Gtk.AboutDialog(transient_for=self.window, modal=True)
159 about_dialog.present()
160
161 def on_quit(self, _action, _param):
162 self.quit()
163
164
165if __name__ == "__main__":
166 app = Application()
167 app.run(sys.argv)