Drag and Drop#
See also
Drag-and-Drop in the GTK documentation.
GTK drag-and-drop works with drag sources and drop targets.
These are event controllers that can be set to any widget using
Gtk.Widget.add_controller(). The data begin moved in the operation is
provided through a Gdk.ContentProvider.
Drag sources#
Gtk.DragSource is the event controller that allows a widget to be used
as a drag source.
You can set up everything needed for the drag-and-drop operation ahead of time
or do it on the fly using the signals provided by Gtk.DragSource.
You can use Gtk.DragSource.set_content() to set the
Gdk.ContentProvider that will be sent to drop targets.
A content provider is usually created using
Gdk.ContentProvider.new_for_value() where you only pass the value to send.
To pass different values for multiple possible targets you can use
Gdk.ContentProvider.new_union() were you can pass a list of
Gdk.ContentProviders.
Gtk.DragSource provides signals for the different stages of the drag
event.
The prepare signal is emitted when a
drag is about to be initiated, here you should return the
Gdk.ContentProvider that will be sent, otherwise the one set with
Gtk.DragSource.set_content() will be used.
The drag-begin signal is emitted
when the drag is started, here you can do things like changing the icon attached
to the cursor when dragging using Gtk.DragSource.set_icon().
Also the drag-end signal is provided,
you can use it to undo things done in the previous signals.
Finally drag-cancel allows you
to do things when the operation has been cancelled.
Drop targets#
Gtk.DropTarget is the event controller to receive drag-and-drop
operations in a widget.
When creating a new drop target with Gtk.DropTarget.new() you should
provide the data type and Gdk.DragAction that your target accepts.
If you want to support multiple data types you can pass GObject.TYPE_NONE
and then use Gtk.DropTarget.set_gtypes() where you can pass a list of
types, be aware that the order of the list establish the priorities.
Gtk.DropTarget provides multiple signals for the process. These are
accept,
drop,
enter,
leave, and
motion.
Generally connecting to drop is only
needed, this signal will receive the value sended by the Gtk.DragSource.
For more complex use cases checkout Gtk.DropTargetAsync.
Example#
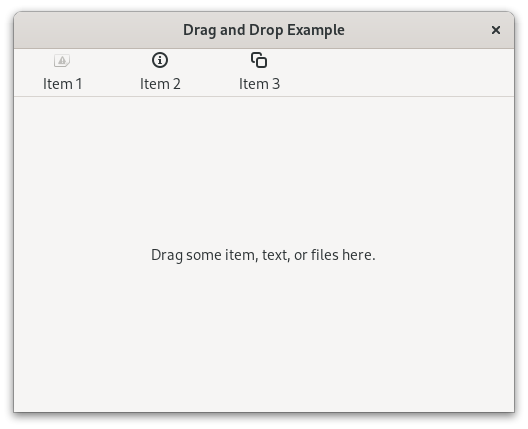
1import gi
2
3gi.require_version("Gdk", "4.0")
4gi.require_version("Gtk", "4.0")
5from gi.repository import Gdk, GObject, Gtk
6
7
8class DragDropWindow(Gtk.ApplicationWindow):
9 def __init__(self, *args, **kargs):
10 super().__init__(*args, **kargs, title="Drag and Drop Example")
11
12 self.set_default_size(500, 400)
13
14 views_box = Gtk.Box(orientation=Gtk.Orientation.VERTICAL)
15 views_box.props.vexpand = True
16 self.set_child(views_box)
17
18 flow_box = Gtk.FlowBox()
19 views_box.append(flow_box)
20 flow_box.props.selection_mode = Gtk.SelectionMode.NONE
21 flow_box.append(SourceFlowBoxChild("Item 1", "image-missing"))
22 flow_box.append(SourceFlowBoxChild("Item 2", "help-about"))
23 flow_box.append(SourceFlowBoxChild("Item 3", "edit-copy"))
24
25 views_box.append(Gtk.Separator())
26
27 self.target_view = TargetView(vexpand=True)
28 views_box.append(self.target_view)
29
30
31class SourceFlowBoxChild(Gtk.FlowBoxChild):
32 def __init__(self, name, icon_name):
33 super().__init__()
34
35 self.name = name
36 self.icon_name = icon_name
37
38 box = Gtk.Box(orientation=Gtk.Orientation.VERTICAL, spacing=6)
39 self.set_child(box)
40
41 icon = Gtk.Image(icon_name=self.icon_name)
42 label = Gtk.Label(label=self.name)
43
44 box.append(icon)
45 box.append(label)
46
47 drag_controller = Gtk.DragSource()
48 drag_controller.connect("prepare", self.on_drag_prepare)
49 drag_controller.connect("drag-begin", self.on_drag_begin)
50 self.add_controller(drag_controller)
51
52 def on_drag_prepare(self, _ctrl, _x, _y):
53 item = Gdk.ContentProvider.new_for_value(self)
54 string = Gdk.ContentProvider.new_for_value(self.name)
55 return Gdk.ContentProvider.new_union([item, string])
56
57 def on_drag_begin(self, ctrl, _drag):
58 icon = Gtk.WidgetPaintable.new(self)
59 ctrl.set_icon(icon, 0, 0)
60
61
62class TargetView(Gtk.Box):
63 def __init__(self, **kargs):
64 super().__init__(**kargs)
65
66 self.stack = Gtk.Stack(hexpand=True)
67 self.append(self.stack)
68
69 empty_label = Gtk.Label(label="Drag some item, text, or files here.")
70 self.stack.add_named(empty_label, "empty")
71 self.stack.set_visible_child_name("empty")
72
73 box = Gtk.Box(
74 orientation=Gtk.Orientation.VERTICAL,
75 vexpand=True,
76 valign=Gtk.Align.CENTER,
77 )
78 self.stack.add_named(box, "item")
79
80 self.icon = Gtk.Image()
81 box.append(self.icon)
82 self.label = Gtk.Label()
83 box.append(self.label)
84
85 self.text = Gtk.Label()
86 self.stack.add_named(self.text, "other")
87
88 drop_controller = Gtk.DropTarget.new(
89 type=GObject.TYPE_NONE, actions=Gdk.DragAction.COPY
90 )
91 drop_controller.set_gtypes([SourceFlowBoxChild, Gdk.FileList, str])
92 drop_controller.connect("drop", self.on_drop)
93 self.add_controller(drop_controller)
94
95 def on_drop(self, _ctrl, value, _x, _y):
96 if isinstance(value, SourceFlowBoxChild):
97 self.label.props.label = value.name
98 self.icon.props.icon_name = value.icon_name
99 self.stack.set_visible_child_name("item")
100
101 elif isinstance(value, Gdk.FileList):
102 files = value.get_files()
103 names = ""
104 for file in files:
105 names += f"Loaded file {file.get_basename()}\n"
106 self.text.props.label = names
107 self.stack.set_visible_child_name("other")
108
109 elif isinstance(value, str):
110 self.text.props.label = value
111 self.stack.set_visible_child_name("other")
112
113
114def on_activate(app):
115 win = DragDropWindow(application=app)
116 win.present()
117
118
119app = Gtk.Application(application_id="com.example.App")
120app.connect("activate", on_activate)
121
122app.run(None)